#nursing pharmacology
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
I Survived My Mom's Nursing Degree Graduation Gift For Women Premium T-Shirt

Product details
Fabric type
Solid colors: 100% Cotton; Heather Grey: 90% Cotton, 10% Polyester; All Other Heathers: 58% Cotton, 42% Polyester
Care instructions
Machine Wash
Origin
Imported
About this item
I Survived My Mom's Nursing Degree Graduation Gift For Women. Happy Graduation celebratory Gifts or Mom's nursing degree Hilarious Congratulate and being a proud dad. Perfect Student School graduation Year Grad men, women senior student registered nurses.
Men Senior Nursing student nursing nursing school university bachelor Class 2024.Mom, daughter, sister, friend, her wife, coworkers, employees, boss, mentor, female, volunteers, friends, staff, officer, member, assistant.
<<<>> Get Access Now <<>>>
#nursing student#nursing school#nursing pharmacology#nursing assessment#nursing#nursing school lessons
1 note
·
View note
Text

I did this instead of studying ya'll.
#studyblr#finals week#I should be studying#nursing school#pathophysiology#pharmacology#foundations of nursing#health assessments#memes#lol#kingdom hearts#IDK which one#will turner#elizabeth swann#orlando bloom#kierra knightley
14 notes
·
View notes
Text
How Does The Drug Got Excreted / Eliminated From The Body?
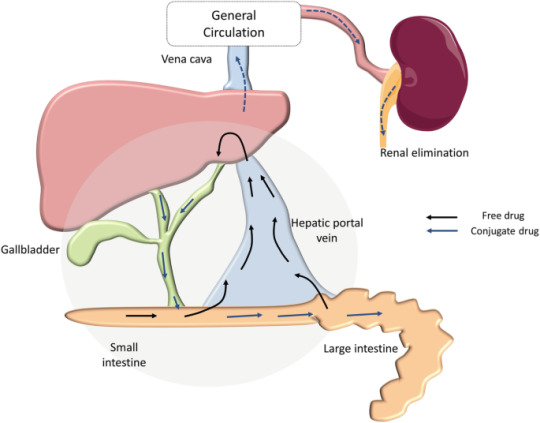
Drug excretion is an important process in pharmacology, encompassing the elimination of pharmaceutical substances from the body. While the ultimate elimination of all drugs is inevitable, the specific pathways involved can vary significantly. Some drugs undergo extensive metabolic transformations before being excreted, while others are expelled from the body in their original form.
The kidneys play a central role in excreting water-soluble substances, effectively filtering them from the bloodstream. Meanwhile, the biliary system handles drugs that remain unabsorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, providing an alternative route for elimination. Although excretion through auxiliary channels such as the intestines, saliva, sweat, breast milk, and lungs is typically minimal, certain volatile anesthetics and residual drug traces in breast milk can have notable impacts, particularly on vulnerable populations such as infants.
Renal excretion constitutes a significant portion of drug elimination, accounting for approximately 20% of the plasma that is filtered through the glomeruli. While most water and electrolytes are reabsorbed back into circulation, polar compounds like drug metabolites are excreted predominantly in urine. However, it’s important to note that renal excretion tends to decrease with age, necessitating careful dosage adjustments for elderly patients to mitigate potential adverse effects.
Numerous factors influence the process of renal excretion, including the extent of protein binding, the degree of drug ionization affecting reabsorption rates, fluctuations in urine pH that can alter excretion dynamics, and the impact of metabolic inhibitors on tubular secretion mechanisms.
Biliary elimination, on the other hand, occurs when drugs traverse the biliary epithelium via active transport mechanisms. However, this process is not without limitations, as transporter saturation can impose constraints on drug excretion rates. Typically, larger molecules containing polar and lipophilic groups are excreted through bile, while smaller molecules tend to favor renal elimination pathways.
In addition to renal and biliary routes, drugs may also be eliminated to varying extents through auxiliary pathways such as saliva, tears, feces, sweat, and exhalation. While the quantities eliminated through these routes are generally minimal, drug excretion in breast milk can pose significant concerns for lactating mothers, potentially exposing nursing infants to pharmacological agents.
Understanding the pharmacokinetic parameters governing drug excretion is paramount for optimizing therapeutic regimens and minimizing the risk of adverse effects. Key parameters include the rate of elimination, clearance, elimination rate constant, and biologic half-life for drugs undergoing first-order elimination kinetics.
In conclusion, drug excretion represents a broad process influenced by a myriad of factors, necessitating comprehensive consideration to ensure the safe and efficacious use of pharmacotherapy.
For medical students navigating the complexities of their studies, Expert Academic Assignment Help serves as a beacon of professionalism and expertise. With a steadfast dedication to excellence and competency, our team provides invaluable support and guidance tailored to your academic needs. Do not hesitate to reach out to us for assistance on your academic journey, email: [email protected]
Your excellence our pride.
#assignment help#medical students#healthcare#nursing school#nursing student#medicine#medication#health and wellness#health#homework help#do your homework#university student#medical school#online writing#academic assignments#academic writing#grad school#pharmacy student#pharmacology#pharmacy technician#pharmacy
23 notes
·
View notes
Text
Calculating Medication Doses [Ex. 2]


Patreon
#studyblr#notes#math#math notes#mathblr#maths#health science#life science#healthcare#nursing#nursing math#math in nursing#pharmacology#pharmacology math#math in pharmacology#math and science#science and math#dosage calculations#calculating dosages#medication calculations#calculating medication#basic math#health science math#math in health science#science#scienceblr#sciblr
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
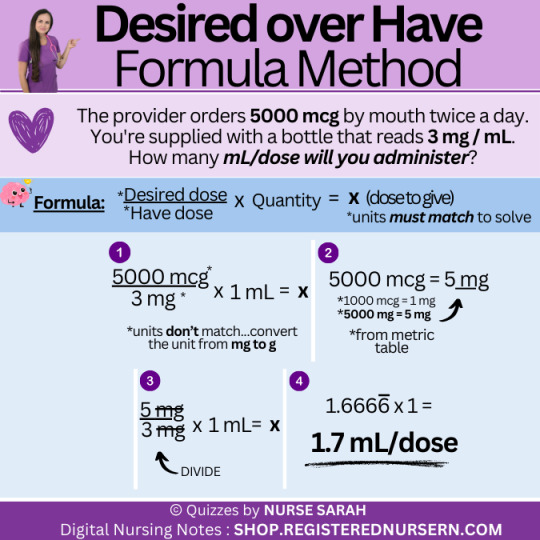
Nursing Dosage Calculations: Liquid Oral Suspensions (Desired Over Have Formula Method)
In this review, I’ll guide you through how to solve liquid oral suspension dosage calculation problems using the desired over have formula method. If you’d like to follow along with me and write down each step of these problems, I have a free dosage calculations worksheet here that you can download. Check out this link for more free nursing dosage calculations reviews. Practice Problem 1: The…
View On WordPress
2 notes
·
View notes
Text


28 June 2023 | Pneumonia
Cardio/pulm are among my top favorites to learn about (ɔ◔‿◔)ɔ♥
#100 days of productivity#notes#study motivation#GoodNotes#student nurse#cardiology#studyblr#pharmacology#pulmonology#napthaliii
35 notes
·
View notes
Text
Got some pretty serious exams at the start of Jan so no more procrastinating with sims for me unless i've done some studying so i'll be posting a lot less. Had to stop taking my anti-anxiety meds to get stuff done bc it makes my ADHD worse and im still waiting for meds on that front. Might be more active next week in the lead up to xmas :)
#hate pharmacology#pray for me#also got pathophyisology to learn and prepping for my OSCE#dies#whos idea was it for me to go nursing school#wish i was rich so i could stay home all day and play sims#nonsims
13 notes
·
View notes
Text
So I have been trying to find a psychiatrist for over a year now, and failing at literally every turn. Finally got an appointment scheduled for a month from now. Just found out that session are going to be $365 until I reach my insurance deductible 🙃 why the fuck would it be that much, I was expecting like $150? And that would have been fine? But $365 for a fucking hour? Absolutely not. I’d rather get a fancy massage.
#cookie speaks#I need help with medication management#but fuck that#I’m a nursing student#I’ve taken pharmacology#I’m taking mental health right now#I’ll figure out my own shut#Jesus Christ
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
Beta-blockers
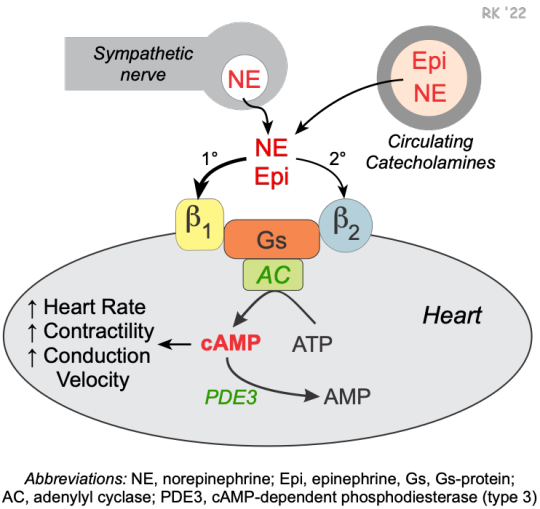
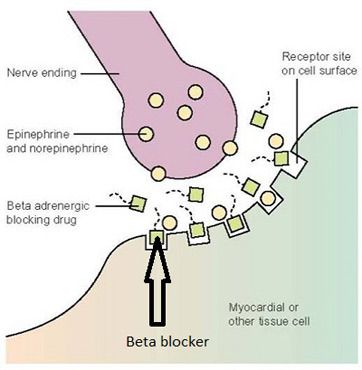
Beta-blockers are a class of medications that are commonly used to treat a variety of conditions such as high blood pressure, heart failure, and angina. These medications work by blocking the effects of the hormone adrenaline, which can help to reduce the workload on the heart and lower blood pressure.
One of the most well-known uses of beta-blockers is in the treatment of performance anxiety. Beta-blockers can be used by musicians, public speakers, and even athletes to help control the physical symptoms of anxiety such as rapid heart rate and trembling hands. By blocking the effects of adrenaline, beta-blockers can help to calm the nerves and improve performance.
Another use of beta-blockers is in the treatment of migraines. Studies have shown that beta-blockers can be effective in reducing the frequency and severity of migraines by reducing the dilation of blood vessels in the brain. Beta-blockers are also sometimes used to prevent the recurrence of heart attacks in patients who have already had one.
While beta-blockers can be effective in treating a variety of conditions, they can also have side effects. Common side effects include fatigue, dizziness, and cold hands and feet. Some patients may also experience depression or nightmares while taking beta-blockers. It's important to discuss the potential benefits and risks of beta-blockers with your healthcare provider before starting any new medication.
In conclusion, beta-blockers are a class of medications that can be useful in treating various conditions, such as high blood pressure, heart failure, and migraines. They can also help manage performance anxiety. However, like all medications, beta-blockers can have side effects and should be used under the guidance of a healthcare provider.
#beta blockers#physiology#pharmacy#pharmacology#medicine#healthcare#health#doctors#disease#nursing#medication#physical health
19 notes
·
View notes
Text

Notes from my 1st yr
#uni#study#nursing#med#medecine#anatomy#anatomy art#pharmacology#study aesthetic#study motivation#studyblr#university#college#art#aesthetic notes#notes#exams#exam revision#revision
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
I can't believe people try to claim nursing isn't a STEM field
#prereqs: bio + anatomy + microbio + algebra and depending on the school also chemistry + pharmacology#degree plan: associate of applied health science OR ASN OR bachelors of science in nursing#literally science is right there in the fucking title like why is it seen as a separate thing?#according to my advisors and teachers its fucking not it literally is a STEM major and qualifies me to apply for STEM specific projects#like i can only guess people want to deny that nursing is a science because they are fucking misogynists or hate their specific nurse#sorry im just having flashbacks to when i got in an argument with someone saying it Isnt part of STEM#and then i googled it to be sure i wasnt tripping and google was like ''nah its not STEM''#its. science. lmao#idk i guess i got an ego boost from that like. im a woman in STEM. 😎
6 notes
·
View notes
Note
LOKI SEASON TWO COMING ONTO DISNEY+ ON OCTOBER 6, 2023! HOW DO YOU FEEL?
I'M SO READY BUT ALSO NOT AT ALL EMOTIONALLY PREPARED BUT ALSO I NEED IT TO COME OUT TODAY AHHHHHHH
#I'm also not financially prepared#I'm trying to save for a trip to disneyland when i graduate next year (or probably a year after than once i have my first real nursing job)#so I've told myself that I'm only allowed to buy new funko pops if they're either Loki or Wanda (or Cassie Lang when she comes out)#but we just got blacklight ragnarok loki and thor 1 jotun loki with the casket which is already too many lokis in a short period#so what am i gonna do when i have the entire season two to buy?#i doubt my brodinsons shelf is even gonna fit them if it's half as many as season one#I'm also trying to be good and not buy more pins#but I've been collecting disney pins foe almost 13 years now and if and when they release loki s2 pins#I'll have no choice but to buy them to add to my marvel pin board y'know?#sorry this is so rambly#i have a pharmacology exam to take and im procrastinating#I'm gonna go do that now#maybe#unless i dont#look i have an ask#loki series
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
Took a pharm test.
Mightve failed
IDK
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
What Are The Stages of Fetal Growth During Pregnancy?
The development of a fetus during pregnancy is a complex and remarkable process, marked by significant changes and growth each month. This journey is typically divided into three stages known as trimesters, each lasting approximately three months. For Healthcare professionals we discuss fetal development in terms of weeks. Here’s a detailed overview of what entails during each month of pregnancy.
a) First Trimester
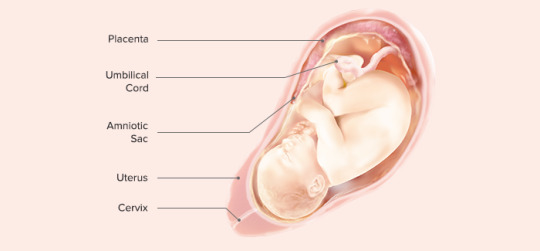
The first trimester of pregnancy encompasses weeks 1 through 12 and is characterized by the initial formation and rapid development of the embryo. This period is critical for establishing the foundation of the future baby’s organs and body systems. The first trimester is often associated with the onset of pregnancy symptoms, such as nausea, fatigue, and hormonal changes.
Month 1 (Weeks 1–4)
Weeks 1–2: The first two weeks of pregnancy are technically considered a preparatory period. During this time, the body releases hormones and prepares the uterus for a potential pregnancy. This period includes ovulation, where an egg is released from the ovary. If fertilization occurs, the zygote forms and marks the beginning of pregnancy.
Week 3: Fertilization occurs when a sperm cell meets the egg, creating a zygote. This single-celled entity undergoes rapid cell division as it travels down the fallopian tube towards the uterus.
Week 4: The zygote becomes a blastocyst, which is a cluster of cells that implants itself into the uterine lining. The amniotic sac and placenta begin to form, playing crucial roles in protecting and nourishing the developing embryo. By the end of this month, the blastocyst is about 2 millimeters long, roughly the size of a poppy seed.
Month 2 (Weeks 5–8)
The second month of pregnancy marks significant developmental milestones as the embryo transitions into more complex forms.
Week 5: The neural tube, which will become the brain and spinal cord, begins to form. The heart, initially a simple tube, starts to pulse, setting the stage for the development of the circulatory system.
Week 6: Limb buds appear, which will eventually become arms and legs. Structures for the ears, eyes, and mouth start to take shape. Blood cells begin to form, and circulation starts within the embryo.
Week 7: The process of ossification starts as bones begin replacing the soft cartilage, and the formation of the genitals commences. The embryo now resembles a tadpole due to its prominent tail.
Week 8: Major organs and body systems continue to develop. The hands and feet start to form web-like structures, and the umbilical cord, which provides nutrients and oxygen to the embryo, is fully developed. By the end of this month, the embryo, now referred to as a fetus, is about 0.5 to 1 inch long, similar to a black bean.
Month 3 (Weeks 9–12)
The third month of pregnancy is marked by significant growth and maturation of the embryo, transitioning into a more recognizable human form.
Week 9: Teeth and taste buds begin to form. The fetus starts developing muscles, and its body takes on a more human appearance, although the head remains disproportionately large.
Week 10: Limbs and digits are fully formed, and the external genitals start to develop, although they are not yet visible on an ultrasound. The placenta continues to grow, providing essential nutrients to the fetus.
Week 11: The fetus begins to move spontaneously, exploring its surroundings by opening and closing its fists and mouth. The bones harden, though the skin remains translucent. Facial features such as the nose and lips become more defined.
Week 12: All essential organs, limbs, bones, and muscles are present and will continue to mature and develop. The fetus is about 2.5 to 3 inches long, roughly the size of a plum. At this stage, the risk of miscarriage decreases significantly, and many women begin to feel relief from early pregnancy symptoms like morning sickness.
Second Trimester
The second trimester of pregnancy spans from weeks 13 to 26. This period is often considered the most comfortable phase of pregnancy as many early symptoms subside, and the risk of miscarriage decreases. The fetus undergoes significant growth and development, and the mother begins to feel fetal movements, known as quickening.
Month 4 (Weeks 13–16)
During the fourth month, the fetus continues to develop rapidly, and its features become more distinct.
Week 13: Vocal cords form, and the fetus’s head starts to grow proportionally to the rest of the body. The fetus begins to practice breathing movements by inhaling and exhaling amniotic fluid, which helps develop the lungs.
Week 14: The skin starts to thicken and fine hair, known as lanugo, begins to grow. The fetus can bring its fingers to its mouth and may start sucking its thumb. External genitals are fully formed, and fingerprints start to develop.
Week 15: The intestines and ears move to their final positions. The fetus practices more purposeful movements, such as thumb-sucking and smiling. The developing nervous system allows the fetus to respond to external stimuli, such as light and sound.
Week 16: The fetus can hear and respond to external sounds. Its eyes, although still closed, can perceive light. By the end of this month, the fetus is about 5 inches long and weighs around 4 ounces, comparable to an avocado.
Month 5 (Weeks 17–20)
The fifth month of pregnancy is marked by increased fetal activity and continued growth.
Week 17: Fat begins to accumulate under the skin, providing insulation and energy reserves. The fetus’s skin is covered with a protective coating called vernix, which prevents it from becoming chapped by the amniotic fluid.
Week 18: The fetus is covered in lanugo, which helps keep it warm and provides an additional layer of protection. The fetus starts to establish a sleep-wake cycle, and its movements become more noticeable to the mother.
Week 19: The fetus’s movements, including kicks and punches, become more frequent and noticeable. Unique fingerprints are fully formed, and the fetus may start to experience hiccups.
Week 20: Nails develop fully, and the sensory areas of the brain mature, allowing the fetus to respond more actively to its environment. By the end of this month, the fetus is about 9 to 10 inches long and weighs around 1 pound.
Month 6 (Weeks 21–24)
The sixth month of pregnancy is a period of significant development, particularly in the nervous and respiratory systems.
Week 21: Coordinated limb movements become more frequent, and the fetus’s bone marrow begins producing blood cells.
Week 22: The fetus’s grasping reflex strengthens, and it can touch its surroundings, including its own body and the umbilical cord. It can hear internal sounds, such as the mother’s heartbeat and external sounds, such as voices and music.
Week 23: The fetus’s viability outside the womb increases, though intensive medical care would be necessary if it were born prematurely. The fetus starts rapidly accumulating fat, which is essential for temperature regulation after birth.
Week 24: Lung development progresses, although the lungs are not yet mature enough for the fetus to breathe independently. The fetus is about 12 inches long and weighs around 2 pounds.
Third Trimester
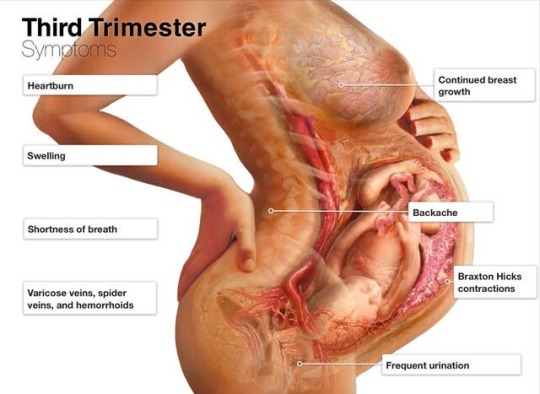
The third trimester of pregnancy spans from weeks 27 to 40 and is characterized by rapid growth and final preparations for birth. During this period, the fetus gains weight quickly and undergoes the final stages of development necessary for survival outside the womb.
Month 7 (Weeks 25–28)
During the seventh month, the fetus continues to grow and develop reserves of body fat.
Week 25: Increased body fat makes the fetus’s skin less wrinkled and more plump. The nervous system matures rapidly, enhancing the fetus’s ability to respond to stimuli.
Week 26: Melanin production begins, contributing to the skin and eye color. The lungs start producing surfactant, a substance that helps the lungs function properly after birth.
Week 27: The fetus’s eyes open, and it develops eyelashes. The fetus begins to develop regular sleep and wake patterns, and its movements become more coordinated.
Week 28: The fetus may begin to position itself head-down in preparation for birth. By the end of this month, the fetus is about 14 to 15 inches long and weighs between 2 to 3 pounds.
Month 8 (Weeks 29–32)
The eighth month of pregnancy involves continued maturation and growth of the fetus, with a focus on brain development.
Week 29: The fetus’s movements become more distinct as space in the uterus becomes cramped. The brain develops rapidly, allowing the fetus to control its body temperature more effectively.
Week 30: The fetus’s brain continues to grow, and it can process information and respond to stimuli. The fetus begins to establish more distinct patterns of activity and rest.
Week 31: The fetus’s skin loses its translucency as fat accumulates beneath it. Most organs, except for the brain and lungs, are fully developed and ready for birth.
Week 32: The fetus is about 17 to 18 inches long and weighs up to 5 pounds. The brain continues to develop rapidly, and the fetus can hear and respond to a variety of sounds.
Month 9 (Weeks 33–36)
During the ninth month, the fetus continues to grow and mature, preparing for birth.
Week 33: The fetus’s bones harden, although the skull remains soft and flexible to facilitate passage through the birth canal.
Week 34: The protective vernix coating thickens, providing additional protection to the fetus’s skin.
Week 35: Brain growth continues, and the fetus’s brain is now capable of regulating essential body functions.
Week 36: The lanugo covering the fetus’s body begins to disappear, and hair growth occurs on the head. The fetus is about 17 to 19 inches long and weighs 6 to 7 pounds.
Month 10 (Weeks 37–40)
The final month of pregnancy is a period of final preparations for birth, with the fetus reaching full maturity.
Week 37: The fetus’s toenails reach the tips of its toes. It continues to gain weight rapidly, preparing for the energy demands of life outside the womb.
Week 38: The fetus’s weight gain continues, and it starts to shed the vernix coating. The fetus moves lower into the pelvis in preparation for birth.
Week 39: The fetus is considered full-term and continues to develop and gain weight. It measures about 18 to 20 inches long and weighs between 7 to 9 pounds.
Week 40: The fetus is ready for birth. Its organs are fully developed and capable of functioning independently. The fetus positions itself head-down in the pelvis, preparing for delivery.
Throughout pregnancy, the fetus undergoes substantial growth and development, preparing for the transition to life outside the womb. Regular monitoring and care by healthcare providers are crucial to ensure the health and well-being of both the mother and the fetus. This comprehensive journey from a single cell to a fully developed baby highlights the incredible complexity of human development.
Expert Academic Assignment Help specializes in supporting medical students to study fetal growth during pregnancy. Our assistance includes study materials, tutoring, assignment help, and exam preparation, ensuring students understand fetal development. We provide mentorship, empowering students to excel academically and become competent healthcare professionals. Email: [email protected]
#medical students#healthcare#nursing school#nursing student#medicine#assignment help#medical student#medical school#medical university#study inspiration#studying#study motivation#study blog#studyblr community#studyblr#studyspo#case study#study notes#student life#student#study aesthetic#academic writing#academic assignments#college student#pharmacology#pharmacy student
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
i am an academic weapon. I AM AN ACADEMIC WEAPON. I AM AN ACADEMIC WEAPON. I AM AN ACADEMIC WEAPON. I AM AN ACADEMIC WE-
8 notes
·
View notes
Text

The beautiful thing about learning is that nobody can take it away from you.
-B.B. King
#studyblr#books#study notes#notes#nursing school#study motivation#original post#library#pharmacology
5 notes
·
View notes